OKRs & KPIs
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
-
Objective: This is a qualitative and inspiring goal that the company wants to achieve. It should be clear and motivating.
-
Key Results: These are quantitative metrics that measure progress towards the objective. They are specific, measurable and have a defined deadline.
-
Example of an OKR in an E-commerce company:
- Objective: Improve the user’s shopping experience on the website.
- Key Result 1: Increase the website conversion rate from 2% to 3% by the end of the quarter.
- Key Result 2: Reduce the cart abandonment rate from 40% to 30% by the end of the quarter.
- Key Result 3: Increase the customer satisfaction score (NPS) from 70 to 80 by the end of the quarter.
- Objective: Improve the user’s shopping experience on the website.
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
-
Key Performance Indicators: These are specific metrics that indicate how well the company is achieving its business objectives. - They monitor the ongoing performance of important processes and activities.
-
Example of KPIs in an E-commerce company:
- Conversion Rate: Percentage of website visitors who complete a purchase.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: Percentage of users who add items to the cart but do not complete the purchase.
- NPS (Net Promoter Score): Measure of customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
E-commerce Context in Software Development
- Context: An e-commerce company wants to improve the user experience on its website, and the software development team is involved in this initiative.
- Defining OKRs
- Objective: Make the checkout process faster and easier.
- Key Result 1: Reduce the average checkout page load time from 5 seconds to 2 seconds in 3 months.
- Key Result 2: Implement a one-click checkout functionality and achieve 50% user adoption in 3 months.
- Key Result 3: Reduce transaction error rate during checkout from 5% to 1% in 3 months.
- Objective: Make the checkout process faster and easier.
- Measuring with KPIs
- Checkout Conversion Rate: Percentage of users who initiate the checkout process and complete the purchase.
- Average Page Load Time: Time it takes for the checkout page to fully load.
- One-Click Checkout Adoption Rate: Percentage of users who use the new one-click checkout functionality.
- Transaction Error Rate: Percentage of transactions that fail during the checkout process.
- Implementation
- Development:
- The development team works to optimize the code and infrastructure to reduce load time.
- Develops and tests the one-click checkout functionality.
- Implements improvements to the payment system to reduce errors.
- Monitoring and Tuning:
- Uses performance analytics tools to monitor page load times.
- Tracks adoption of the new functionality through usage analytics.
- Monitor the error rate in transactions and make adjustments as needed.
- Development:
- Assessment:
- At the end of the 3-month period, the team assesses whether the key results were achieved.
- Adjusts strategies based on the results for the next OKR cycles.
This continuous cycle of setting OKRs and monitoring KPIs helps the company stay focused on clear objectives and measure progress efficiently, adapting quickly to market and customer needs.
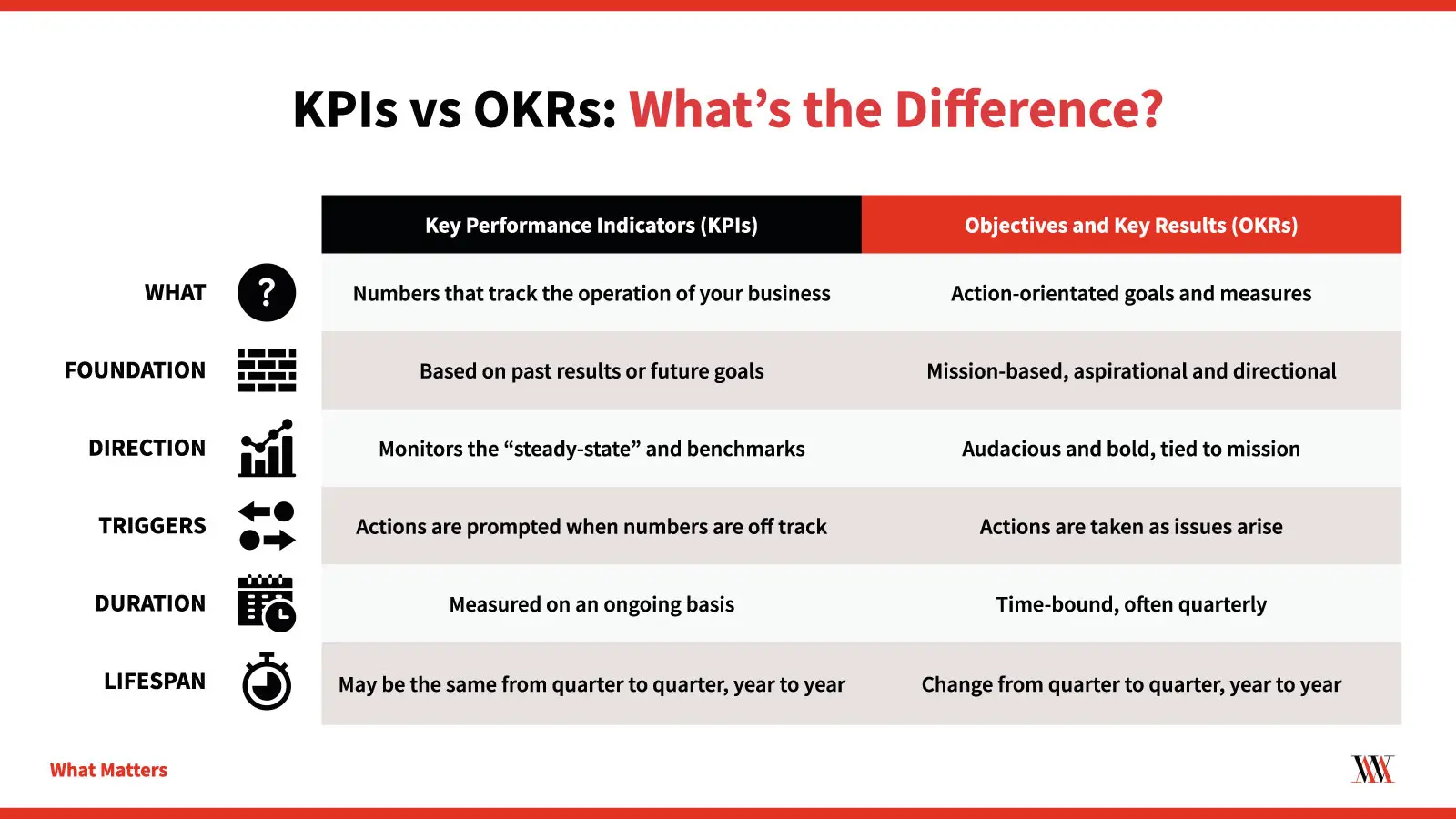
S.M.A.R.T Goals